Static holds for upper body strength are incredibly effective for building muscle and boosting endurance without endless repetitions. These isometric power exercises focus on maintaining a static position under tension, forcing your muscles to fully engage and sustain resistance, which builds strength and enhances muscle stability and endurance. Whether you’re aiming to break through a stubborn strength plateau or seeking a new challenge for your upper body workouts, static holds offer a unique and powerful approach.
By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you can target your muscles in ways that traditional exercises often miss, leading to noticeable improvements in strength and muscle definition. Dive into this article to discover how static holds for upper body strength can transform your training and help you reach your fitness goals.
Static Holds for Upper Body Strength: Mastering Isometric Exercises for Power

Static holds are a powerful way to build upper body strength without moving a muscle. These isometric exercises involve holding a position for a set time, challenging your muscles to maintain tension. Static holds can increase muscle endurance, improve stability, and boost strength in your arms, shoulders, and core.
You might wonder how staying still can make you stronger. When you do static holds, your muscles work hard to keep your body in place. This constant tension helps build strength and stamina. Plus, static holds are great for people of all fitness levels. You can do them at home with little or no equipment.
Ready to take your upper body workout to the next level? Static holds for upper body strength offer a simple yet effective way to challenge your muscles. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced athlete, adding these exercises to your routine can help you see real gains in strength and stability.
Key Takeaways
- Static holds effectively increase muscle strength by maintaining tension in a fixed position, enhancing endurance and muscle stability.
- These exercises help to boost muscle endurance and overall strength by working muscles continuously without rest.
- Many static holds can be performed at home with minimal or no equipment, making them accessible for all fitness levels.
- Static holds strengthen the muscles around joints, improving stability and reducing the risk of injury.
- Individuals can improve their overall body awareness and coordination by focusing on precise muscle control during static holds.

Benefits of Static Holds

Static holds offer several key advantages for building upper body strength. They help increase muscle power, improve joint stability, and enhance body control. These benefits make static holds a valuable addition to any strength training routine.
Muscle Strength and Endurance
Static holds boost muscle strength and endurance effectively. When you hold a position, your muscles work continuously without rest. This constant tension leads to muscle fiber growth and increased strength. Some key benefits include:
- Improved time under tension
- Enhanced muscle activation
- Increased metabolic stress
Static holds for upper body strength are especially good for targeting specific muscle groups. For example, a chin-up hold works your biceps and back muscles intensely. This focused effort can lead to faster strength gains in those areas.
You can also use static holds to break through plateaus in your training. You can stimulate growth and progress by challenging your muscles in a new way.
Joint Stability
Static holds can significantly improve your joint stability. When you hold a position, the muscles around your joints work together to maintain that stance. This cooperation helps strengthen the connective tissues around your joints. Benefits for joint stability include:
- Reduced risk of injury
- Improved balance and coordination
- Better posture
For example, a plank hold engages your core muscles. This engagement helps stabilize your spine and pelvis. Over time, this can lead to better posture and reduced back pain. Static holds are also useful in injury recovery. They allow you to strengthen muscles and joints without too much stress.

Body Control Improvement
Static holds can significantly enhance your body control. By maintaining a specific position, you learn to control your muscles more precisely. This improved control transfers to other exercises and daily activities. Key improvements in body control include:
- Better mind-muscle connection
- Increased proprioception (awareness of body position)
- Enhanced overall stability
For instance, a handstand hold requires you to balance your entire body. This exercise improves your awareness of your body’s position in space. You’ll notice better balance and control in other activities, too.
Static holds also help you focus on proper form. Holding a position lets you feel which muscles should be engaged. This awareness can improve your technique in other exercises.
Essential Static Holds for Upper Body
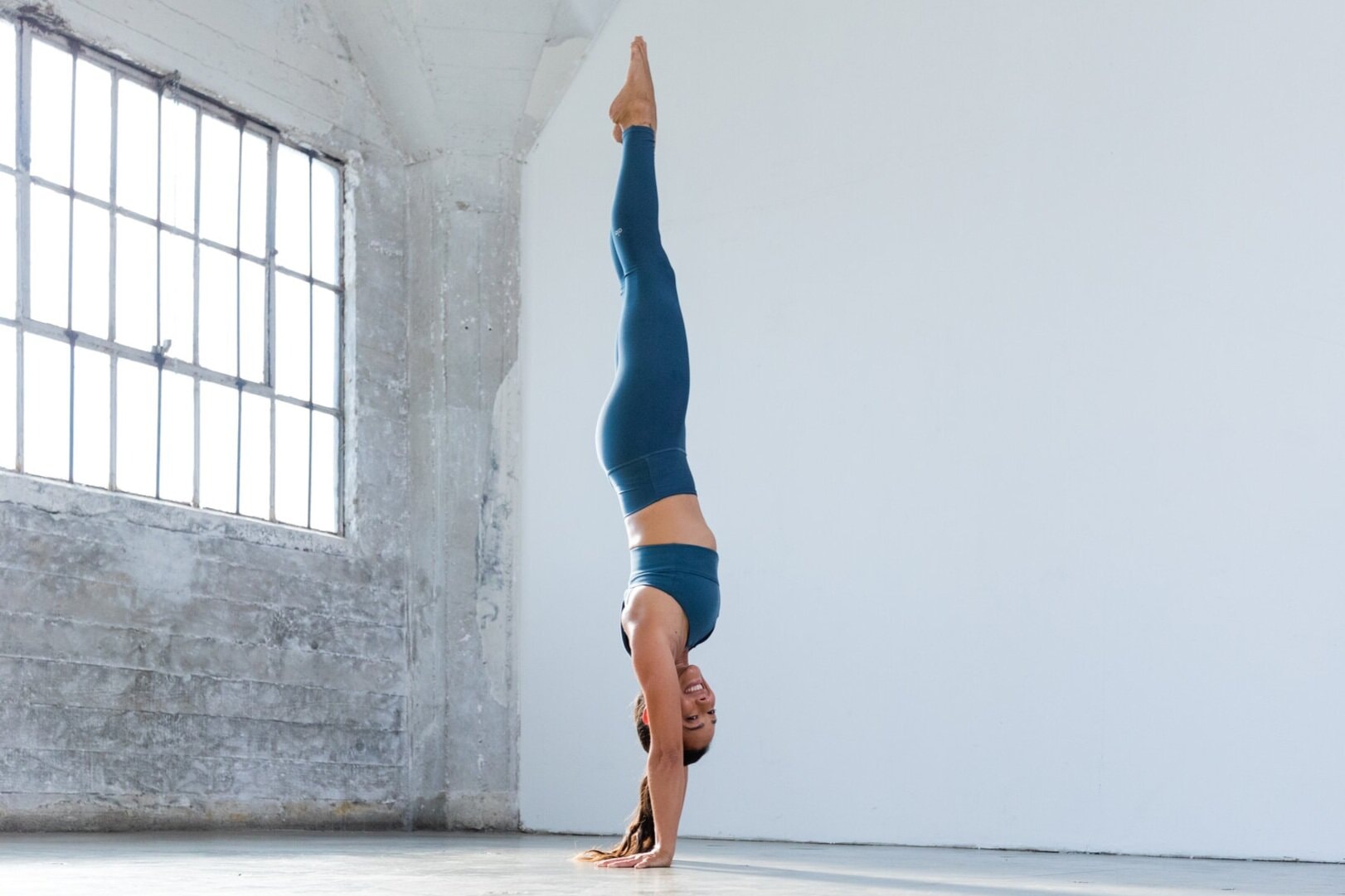

Static holds for upper body strength can build both strength and stability in your upper body. These exercises challenge your muscles without movement, improving endurance and control. Try these key static holds to boost your upper body strength.
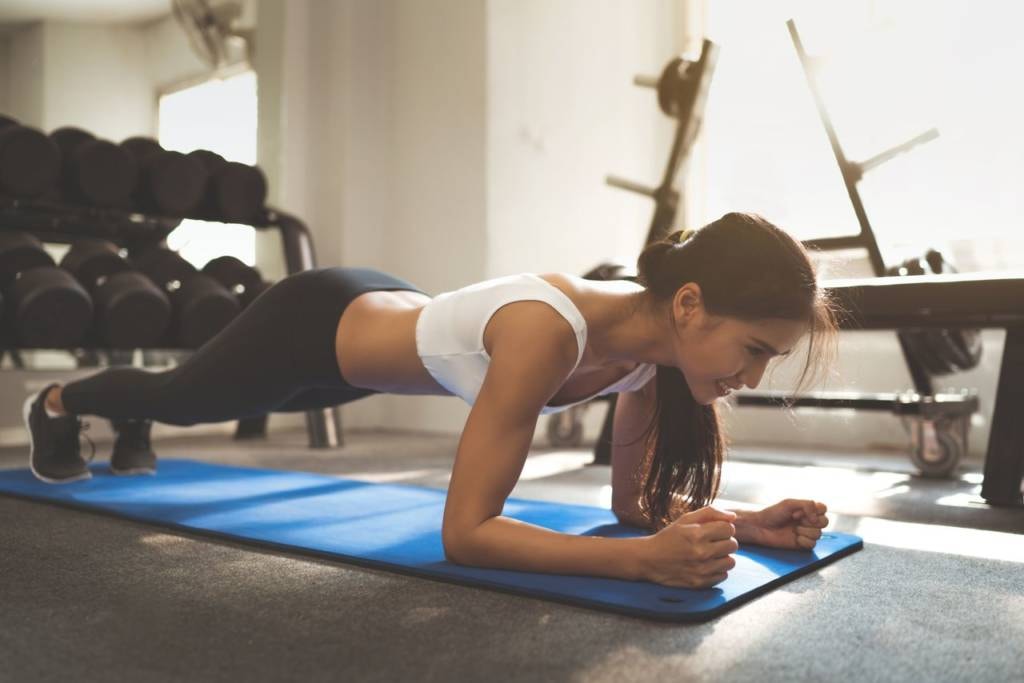
Plank Variations
The plank is a versatile static hold for your upper body and core. Start with a basic high plank, hands under shoulders, and body in a straight line. Hold for 30-60 seconds. For more challenges, try a forearm plank. Lower onto your forearms, keeping your body straight. This targets your shoulders and core even more.
Side planks work your obliques and shoulders. Balance on one forearm, stack your feet and lift your hips. Hold each side for 30 seconds. For an advanced move, try a plank with arm or leg lifts. Lift one limb at a time while keeping your body stable. This tests your balance and strength.
Handstand Hold
Handstand holds build incredible upper body and core strength. Start against a wall for support. Place your hands about 6 inches from the wall, kick up, and find balance. Focus on keeping your body straight and engaged. Press through your shoulders and fingers.
Start with 10-second holds and work up to longer times. If full handstands are too tough, try pike holds. Put your feet on a box or bench, walk your hands in, and lift your hips. This mimics the handstand position, which requires less balance.
Chin-Up Bar Hold
The chin-up hold is great for building grip and arm strength. Jump up to grab the bar with palms facing you, chin above the bar. Hold this position as long as you can. Aim for 20-30 seconds to start. Keep your core tight and your shoulders down away from your ears.
For variety, try different grip widths. A wide grip targets your back more, while a close grip hits your biceps harder. You can also do dead hangs, just hanging from the bar with straight arms. This improves grip strength and stretches your lats.

Did You Know?
The addition of overhead static holds significant benefits for shoulder strength. Overhead static holds, such as barbell holds, greatly improve shoulder stability and strength by targeting the deltoids and rotator cuff muscles. These exercises also enhance the ability to maintain proper form during other overhead movements.
Here’s an additional video featuring a 10-minute isometric upper body workout.
By: Caroline Girvan
Techniques for Proper Form

Good form is key for getting the most out of static holds for upper body strength. Pay attention to your body position, breathing, and how you increase difficulty over time.
Alignment and Posture
Keep your body aligned during static holds. Stand or sit tall with your shoulders back and down for upper body exercises. Engage your core muscles to stabilize your spine. In a plank hold, form a straight line from head to heels. Don’t let your hips sag or your back arch. Keep your back flat against the wall and thighs parallel to the floor for wall sits.
During chin-up holds, pull your shoulder blades down and back. Keep your elbows close to your body, not flared out to the sides. For handstand holds, stack your body in a vertical line. Point your toes up and keep your legs straight and together.
Breathing Patterns
Breathe steadily during static holds. Don’t hold your breath, as this can raise blood pressure. Instead, use slow, controlled breaths. Try to inhale through your nose and exhale through your mouth. This can help you stay relaxed and focused.
Aim for about 2-3 seconds per breath cycle for most holds. As you get tired, you may need to breathe faster. That’s okay. Just keep your breathing smooth and even. Some exercises may affect your breathing. In a hollow hold, for example, your abs are tight. This can make deep breaths harder. Focus on steady, shallow breaths in this position.
Progressive Overload Principles
Start with short hold times and gradually increase. Begin with 10-20 second holds. Add 5-10 seconds each week as you get stronger. Increase difficulty by changing your body position. For planks, move from knees to toes. For wall sits, lower your body closer to the ground. Add weights to make holds harder. Use a weight vest or hold dumbbells.
In a front-rack hold, use heavier kettlebells over time. Try more complex variations as you improve. Move from regular planks to one-arm planks. Progress from chin-up holds to muscle-up holds. Track your progress. Write down hold times and weights used. This helps you see improvement and plan future workouts.
Training Protocols

Static holds for upper body strength can build muscle effectively when done correctly. The right mix of frequency, intensity, and recovery is key to maximizing the benefits. Here are some protocols to follow for the best results.
Frequency and Duration
Do static hold exercises 2-3 times per week. This gives your muscles time to recover between sessions. Each hold should last 10-30 seconds. Beginners can start with 10-second holds and work up from there. For each exercise, do 3-5 sets.
Rest 30-60 seconds between sets. A full static hold workout takes about 20-30 minutes. Try to increase your hold times gradually. Add 5 seconds each week until you reach 30-second holds. This steady progress helps build strength over time.
Intensity Levels
The right intensity is crucial for static holds. You want to challenge your muscles without overdoing it. Use a weight that lets you hold the position for the target time. For example, if your goal is a 20-second hold, pick a weight you can have for precisely 20 seconds.
As you get stronger, increase the weight to keep the challenge high. Aim for a weight that creates muscle failure by the end of your target hold time. Adjust your body position to change the intensity for bodyweight holds like planks or pull-up holds.
Rest and Recovery
Proper rest between workouts is vital for strength gains. Give your upper body at least 48 hours of rest between static hold sessions. This allows your muscles to repair and grow stronger. During workouts, rest 30-60 seconds between sets. This short break helps you maintain good form for each hold.
Listen to your body. If you feel very sore, add an extra rest day. Pushing too hard can lead to injury or burnout. Good sleep and nutrition also play a significant role in recovery. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Eat plenty of protein to support muscle repair.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Static holds can boost upper body strength, but some errors can hinder progress. Watch out for these common pitfalls to get the most from your training.
Overtraining
Pushing too hard with static holds for upper body strength can lead to burnout. Your muscles need time to recover and grow stronger. Don’t do static holds every day for the same muscle groups. Give each muscle group at least 48 hours of rest between workouts. This lets your body repair and build new muscle tissue. Pay attention to signs of overtraining:
- Constant muscle soreness
- Feeling tired all the time
- Decreased performance
Take a break and adjust your workout plan if you notice these symptoms.
Improper Progression
Many people need to avoid holding static positions for too long too soon. This can lead to injury or muscle damage. Start with shorter hold times and gradually increase. A good rule is to add 5-10 seconds each week. Use this simple progression plan:
- Week 1: 20-second holds
- Week 2: 25-30 second holds
- Week 3: 35-40 second holds
Listen to your body. If a hold feels too easy, increase the time. If it’s too hard, decrease it.
Neglecting Accessory Moves
Focusing only on static holds can limit your upper body strength gains. Include other exercises to target all muscle groups and movement patterns. Mix in dynamic exercises like:
- Push-ups
- Pull-ups
- Rows
- Shoulder presses
These moves complement static holds and help build well-rounded strength. They also prevent muscle imbalances that can lead to injury. Try to balance your workout with 50% static holds and 50% dynamic exercises. This approach ensures you’re working your muscles differently for optimal strength gains.
Incorporating Static Holds Into Workout Routines

Static holds for upper body strength can significantly enhance your workout plan. These exercises make your muscles work hard without moving, providing a powerful way to build strength and endurance.
By incorporating static holds into your routine, you can effectively target your upper body muscles and achieve greater results. You can use them in different ways to get the most benefit and elevate your fitness regimen.
Superset Strategies
Supersets with static holds can make your workouts more intense. Try doing a regular exercise, then a static hold right after. For example, do push-ups, then hold a plank. You can also mix static holds with dynamic moves. Do a chin-up, then hold at the top for 10 seconds. This works your muscles in two ways at once.
Another option is to do a static hold between sets of a regular exercise. Hold a dumbbell overhead for 30 seconds between sets of shoulder presses. This keeps your muscles working even during rest periods.
End-of-Workout Finishers
Static holds make great finishers for your workouts. They push your muscles to their limits at the end of your session. Try a wall sit for 60 seconds after leg day. Hold the top of a pull-up for the upper body as long as you can.
These challenges test your endurance and strength. You can also do a circuit of short holds. Move through 15-second holds of plank, hollow hold, and barbell hold. Repeat the circuit 3 times for a tough finish.
Active Recovery Implementation
Static holds can help on rest days, too. They keep your muscles engaged without tiring you out too much. Do a set of gentle holds as part of your active recovery. Try a light kettlebell front rack hold for 30 seconds. This works your core and upper body without strain.
You can also use static holds to improve posture. Hold a band pull-apart position for 20 seconds. This strengthens your back muscles and helps with shoulder stability. Remember to keep the intensity low on recovery days. The goal is to move and maintain strength, not to push to your limits.
Advanced Techniques

Static holds for upper body strength can be more challenging to improve your muscle power further. These methods push your muscles to new limits and enhance overall performance.
Weighted Variations
- Add weights to your static holds.
- Use a weight vest or hold dumbbells during planks.
- For pull-up holds, wear a dip belt with plates attached.
- Start with light weights and slowly increase as you get stronger.
Weighted holds boost muscle tension and force production. They help build strength faster than body weight alone. Be careful not to put too much weight on too soon. Proper form is key to avoiding injury.
Balancing Challenges
Adding instability makes static holds harder. Try pull-up holds on gymnastic rings instead of a fixed bar. Push-up holds should be made with your hands on medicine balls. For planks, put your feet on a stability ball.
These unstable surfaces engage more muscles. Your core works extra hard to keep you steady. Start with short holds and build up time as you improve. Always have a spotter nearby when trying new balance challenges.
One-Limb Static Holds
Single-arm or single-leg holds are very tough. They build strength and fix muscle imbalances. Try a one-arm push-up hold or single-leg plank. For pull-ups, do a one-arm hang.
These exercises require great strength and control. Start with very short holds, like 5-10 seconds. Slowly add time as you get stronger. Always warm up well before attempting one-limb holds. If you feel pain, stop right away.

Check out this video featuring static stretching for the upper body, with arm stretches for both men and women post-workout.
By: COACH ALI
Harnessing the Power of Static Holds: Enhancing Upper Body Strength
Static holds for upper body strength offer a powerful and efficient method for building muscle endurance and stability. These isometric exercises challenge the muscles by maintaining a static position under tension, enhancing muscle strength, and improving overall performance and stability. By incorporating static holds into a fitness routine, individuals can target specific muscle groups effectively, leading to noticeable improvements in muscle definition and strength. Additionally, these exercises can help develop mental toughness, requiring sustained focus and effort to maintain the hold.

Static holds are a valuable addition to any workout regimen, especially for those looking to overcome training plateaus or add a new dimension to their exercises. Individuals can achieve a more balanced and comprehensive strength-building approach by complementing dynamic movements with static holds. These exercises also promote better joint stability and body control, essential for overall functional fitness. Embracing static holds can transform fitness routines, helping individuals reach their fitness goals and enhance their overall physical capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions

What Are the Most Effective Static Holds to Increase Upper Body Strength?
High planks are excellent for strengthening the shoulders, chest, and core. Chin-up holds work the biceps and back muscles. Wall handstands challenge your shoulders and arms. These exercises engage multiple muscle groups at once.
How Do Static Holds Compare to Isotonic Exercises for Muscle Growth?
Static holds increase time under tension, which can lead to muscle growth. They complement dynamic exercises by improving muscle endurance and stability. Both types of exercises have their place in a well-rounded strength training program.
Can Static Holds Be Effectively Performed at Home Without Equipment?
Yes, many static holds require little to no equipment. Push-up holds, wall sits, and doorway chin-up holds can all be done at home. These exercises use your body weight as resistance, making them accessible and effective.
What Are the Specific Benefits of Including Static Holds in Your Workout Routine?
Static holds improve muscle endurance and strengthen connective tissues. They enhance mind-muscle connection and boost overall strength. Static holds also help correct imbalances and improve posture.
Which Muscles Are Primarily Targeted During Upper Body Static Holds?
Upper body static holds mainly target the shoulders, chest, arms, and back. Planks work the chest and shoulders. Chin-up holds engage the biceps and back. Wall handstands challenge the shoulders and triceps.
Stay Active and Inspired: Become a Part of the Fit After 55 Community!
Discover a wealth of fitness inspiration at Fit After 55!
Visit our website (https://www.vitalityseniorliving.com/resources_for_senior/staying-fit-at-55/) for engaging content, expert tips, and product reviews tailored for seniors. Connect with our supportive Facebook community (https://www.facebook.com/fitafter50dotcom/) to engage with others who are committed to a healthy, active lifestyle.
Join us on this fitness journey and prove that age is just a number!